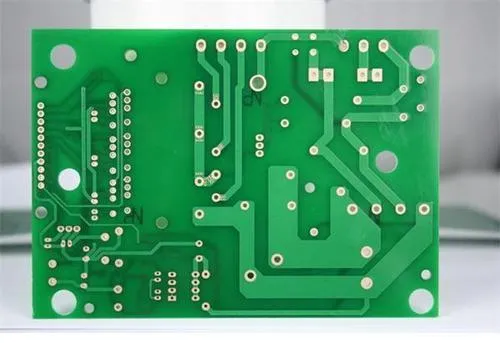
Why the common thICkness of PCB manufacturers is 1.6mm
Information summary:
The general thickness of finished PCB boards is between 0.8mm and 1.6mm, while the more common board thickness is designed in metric units of 1.6mm (about 63mil in English units) by default. Many connector standards are also adapted to the 1.6mm specification. How does the 1.6mm thickness standard come from? Today, I will show you the origin of this standard
In the era of electronic tubes, the PCB industry was still in its infancy. Due to the large heat generation of electronic tube components and their bulky size, it was not convenient to install them on the printed circuit board (a certain mechanical strength was required). At that time, the production and manufacturing of electronic products were basically manual installation in a shed. Of course, this was also related to the development of PCB substrate materials. Epoxy resin as PCB substrate Copper foil and other manufacturing technologies have not yet achieved commercial production.
Phenolic laminate is a solid and good insulating polymer material, which has the characteristics of heat resistance, water resistance, chEMIcal resistance and high current resistance. Although it is not specially developed for the use of circuit boards, it is more widely used for decorative panels, but its strength is much better than gypsum board, cardboard, or wood veneer, whether it is drilling performance or as the installation support of electronic tubes, Therefore, it is natural for PCB manufacturers to choose phenolic laminates as circuit boards instead of cardboard or veneer.
However, it is still a very laborious thing to punch holes in the phenolic laminate and then connect all electronIC components together by wiring, which is more laborious than playing with the hole board. After all, the hole board is perforated in advance. It didn't take long for someone to come up with a method to stick a piece of copper foil on the phenolic laminate, and then etch the interconnection lines between components on the copper foil (in 1913, Berry of Britain invented the technology of coating the metal foil with an anti-corrosive agent, and then etching the uncoated part to form a conductive pattern), which made a single-sided printed circuit board. Soon, the development of the interconnection system between multiple circuit boards has generated the demand for board to board connectors.
While 1/16 inch or 63mil is the production thickness of phenolic laminate at that time. The board to board connector is naturally designed according to 1/16 inch (about 63mil or 1.6mm) plate thickness, which forms a supporting industry chain. 1/16 inch (about 63mil or 1.6mm) plate thickness has also become the industry default standard.
Today, the development of substrate materials has been very diversified, but 1.6mm (or 63mil in imperial units) is still the default finished plate thickness of PCB manufacturers, but the standard plate thickness range has been expanded to 0.8mm~1.6mm. (The specific process of the plate factory shall prevail, and some plate factories are 0.6mm~2.5mm)
Of course, it is also possible to produce thinner or thicker PCBs (such as 20 ply boards), such as 0.4mm or 3.0mm, but the cost of the boards needs to be paid additionally, so customers need to consider when designing PCBs.
When determining PCB thickness, many design and manufacturing factors need to be considered, such as:
Copper thickness
board
Number of layers of PCB
Signal type
Type of through-hole
Operating environment
Manufacturing factors affecting PCB thickness include:
Process capability of drilling equipment
Copper thickness
Number of layers
Splitting method
Factors to be considered when designing PCB with non-standard thickness:
1. Process capability of Pcb factory
The first thing to consider is whether your board factory has the equipment to manufacture the circuit board thickness you need. This decision should be made as early as possible in the design process, taking into account the design requirements of other relevant DFMs. Otherwise, you may be forced to modify and redesign your PCB stack structure.
2. Extension of delivery time
If the materials that are not always available in the board factory are selected, the production cycle of PCB will often be prolonged, so the delivery time needs to be considered for non-standard board thicknesses.
3. Additional expenses
This is probably the most important point. You need the cost of special plates, additional manufacturing costs and extended delivery time costs to determine whether the additional costs are acceptable.
Preferential use of standard PCB thickness will enable your board to be manufactured faster and at lower cost. However, if you decide to choose non-standard thickness, you should have time to communicate with the board factory before starting PCB design, to ensure that the process of the board factory can be manufactured, and to communicate the delivery time and additional manufacturing costs.
然后
聯(lián)系
電話熱線
13410863085Q Q
微信

- 郵箱